TU Wien:Introduction to Security VU (Maffei)/Prüfung 2021-06-25
CSRF[Bearbeiten | Quelltext bearbeiten]
Which of the following can be used as a protection or mitigation mechanism against CSRF attacks?
- The HttpOnly cookie attribute
- The validation of the Referer HTTP header.
- The SameSite cookie attribute
- The web application embeds secret, randomly generated tokens into the HTML forms to be protected. When a request is received, the application checks for the presence of the token before processing it.
- The Content Security Policy.
- The Secure cookie attribute
Cookie jar[Bearbeiten | Quelltext bearbeiten]
The cookie jar of a browser contains the following cookies:
| Name | Value | Domain attribute | Domain who set the cookie | Path | Secure | HttpOnly | SameSite |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| sid | xyz123 | not set | example.com | / | yes | yes | Lax |
| lang | en | example.com | prefs.example.com | / | no | no | Lax |
| admin | abc456 | not set | example.com | /admin | yes | yes | Strict |
Which cookies are attached to a request from https://site.com to https://www.example.com/admin/index.php? Assume that the request been triggered by the user clicking on a link on https://site.com, i.e., it is a top-level navigation.
- lang
- sid
- admin
User’s Browser[Bearbeiten | Quelltext bearbeiten]
Which of the following web attacks involve the user’s browser as part of the attack flow?
- Command Injection
- Reflected Cross-Site Scripting
- Path Traversal
- Stored Cross-Site Scripting
- Cross-Site Request Forgery
ECB[Bearbeiten | Quelltext bearbeiten]
In the Electronic Codebook (ECB) encryption mode…
- Decryption cannot be parallelized.
- Identical blocks in the plaintext result in identical blocks in the ciphertext.
- If one bit in the first block of the ciphertext gets corrupted, none of the plaintext blocks can be recovered.
- Encryption cannot be parallelized.
- Random read access is possible.
Prepared Statements[Bearbeiten | Quelltext bearbeiten]
Which claims about prepared statements are correct (assuming a correct usage)?
- Prepared statements are more effective if malicious characters are filtered out before their usage.
- Prepared statements are used to prevent stored XSS.
- Prepared statements remove all special characters from user input.
- Prepared statements guarantee the structural integrity of a SQL query.
iFrame[Bearbeiten | Quelltext bearbeiten]
The page at https://www.example.com/admin/index.php contains a frame whose source attribute can be chosen among the URLs below. Assume that the frame executes a script which tries to access the DOM of the page embedding the frame. For which URLs does the operation succeed?
- https://www.example.com:443/index.php
- https://example.com/list.php?name=matteo
- http://www.example.com/admin/index.php
- https://www.example.com/list.php?name=karl
Protocol[Bearbeiten | Quelltext bearbeiten]
Consider the following protocol, where we use
- skA to denote A’s private signing key,
- pkB to denote B’s public encryption key,
- sign(m;k) for a message m signed with the private signing key k,
- enc(m;k) for a public key encryption of message m with public key k.
- n for a nonce.
A B
<— A,B,n —
— enc(m,sign(n,m;skA);pkB) —>
Which of the following statements about the protocol are true?
- The protocol ensures the confidentiality of the message m.
- The protocol provides non-injective agreement: whenever B authenticates m as coming from A, A has really started an session with B to authenticate m). However, it does not provide injective agreement.
- The protocols provides injective agreement: whenever B authenticates the message m as coming from A, A has really started a session with B to authenticate m and the authentication request is fresh.
XSS[Bearbeiten | Quelltext bearbeiten]
Which of the following claims about XSS are true?
- XSS attacks are not possible if the HTTPS protocol is used.
- Cookies marked as HttpOnly cannot be read from the cookie jar in a XSS attack.
- It is sufficient to remove <script> tags from user input to prevent all XSS attacks.
- Reflected XSS attacks are impossible if a webpage does not use GET-parameters.
2-factor authentication[Bearbeiten | Quelltext bearbeiten]
Which of the following combinations can be used to implement 2-factor authentication (2FA)?
- Password + key stretching
- Password + authenticator app
- Fingerprint + hardware token
- OTP + CAPTCHA
Subsititution Cipher[Bearbeiten | Quelltext bearbeiten]
The following message has been encrypted with a substitution cipher:
PBBDCT
Which of the following could be the corresponding plaintext message?
- ALERTS
- ACCEPT
- ASSERT
- ERRORS
Unix Permissions[Bearbeiten | Quelltext bearbeiten]
Assume the following output of the ls command displaying the permissions of the standard rm binary:
-rwsr-x-w- 1 root users 72056 Sep 5 2019 /usr/bin/rm
Which of the following statements are true?
- The user jane, who is not a member of the users group, can execute the rm binary
- The root user can not execute the rm binary
- The permissions allow unprivileged users (i.e., users other than root and members of the users group) to cause severe damage in the system
- The user john in the users group can execute rm to delete any file owned by root
Stack canaries[Bearbeiten | Quelltext bearbeiten]
Which of the following statements about stack canaries are correct?
- Stack canaries are an effective mitigation against heap overflow vulnerabilities
- Given this vulnerable function call in C memcpy(dest, src, strlen(src)+1), where the attacker controls dest and the content of src, stack canaries prevent attackers from overwriting the return address of the current function
- Stack canaries do not prevent attackers from overwriting variables in the same stack frame
- The protection mechanism is voided if an attacker overwrites the stack location containing the canary value
PHP[Bearbeiten | Quelltext bearbeiten]
Consider the following snippet of code:
<?php
$db = new PDO(CONNECTION_STRING, DB_USER, DB_PASS);
$query = "SELECT name, mail_address FROM users WHERE POSITION(?, name) > 0";
$sth = $db->prepare($query);
$sth->bindValue(1, $_GET["search"]);
$sth->execute();
echo "Results for " . $_GET["search"];
foreach ($sth as $row) {
echo "Name: " . $row["name"];
echo "Mail address: " . $row["mail_address"];
}
?>
Which of the following statements are true?
- The code is vulnerable to command injection.
- The code is secure.
- The code is vulnerable to SQL injection.
- The code is vulnerable to reflected XSS.
- The code is vulnerable to path traversal attacks.
RSA & OEAP[Bearbeiten | Quelltext bearbeiten]
Consider an encryption scheme based on RSA with OEAP padding. We write E(m, k) to denote the encryption of message m under the public key k = (e, N). Which of the following statements are true?
- Given E(m, k) where the message m is much smaller than the modulus N and e=3, it is easy to recover m.
- The multiplicative property of RSA holds, i.e., E(m1, k) * E(m2, k) = E(m1*m2, k) for any m1, m2.
- OEAP introduces randomness in the ciphertext.
Bruteforce[Bearbeiten | Quelltext bearbeiten]
Which techniques can be used to reduce the likelihood of a successful bruteforce attack against a login form on a website?
- Password salting
- Cascade hashing (~1M iterations) during the authentication phase
- 2-factor authentication
- CAPTCHA
Type system 1[Bearbeiten | Quelltext bearbeiten]
Consider the following information flow type system presented during the lecture.
Which types of information leaks can be detected by it?
- Explicit information flows, i.e., assignment of a secret (high) value to a public (low) variable.
- Information flows via termination channels.
- Implicit information flows where the value of a public variable is assigned within a conditional statement whose condition involves a secret variable.
- Information flows via timing channels.
W^X[Bearbeiten | Quelltext bearbeiten]
Which of the following statements about W^X/DEP are correct?
- W^X/DEP prevents the stack from being corrupted to alter the control flow of the application
- Code reuse attacks are not mitigated by W^X/DEP
- W^X/DEP protects against code injection
- W^X/DEP works by randomizing the writable memory
Declassification[Bearbeiten | Quelltext bearbeiten]
Which of the following statements regarding declassification are correct?
- A typical use case of declassification is the case of password checking, where the result of a comparison involving a secret (i.e., the password) is treated as a public value.
- Declassification is used in information flow type systems to explicitly allow some form of information leaks in programs.
- Improper usage of declassification may introduce security vulnerabilities in programs.
C[Bearbeiten | Quelltext bearbeiten]
Consider the following C program:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int
valid_username(void) {
char username[16];
gets(username);
if(strlen(username) > 15) {
return 0;
} else {
return 1;
}
}
int
main(void) {
if(valid_username()) {
printf("All fine!\n");
};
return 0;
}
Which of the following statements are correct?
- The input “Markchristopher” does not cause a buffer overflow
- The correct way to enforce bound-checking is to truncate the username array after the gets call
- The fundamental problem is the limited array length of the variable username: increasing the length solves the problem
- The input “supercalifragilisticexpialidocious” does not cause a buffer overflow because the user input is ensured to be shorter than 16 bytes
Type system 2[Bearbeiten | Quelltext bearbeiten]
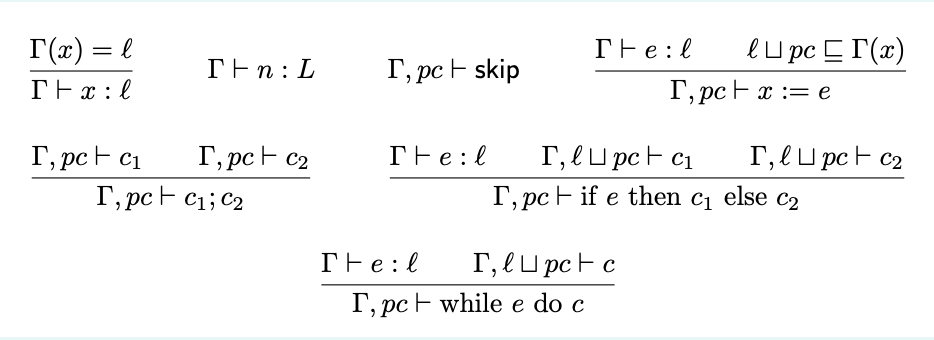
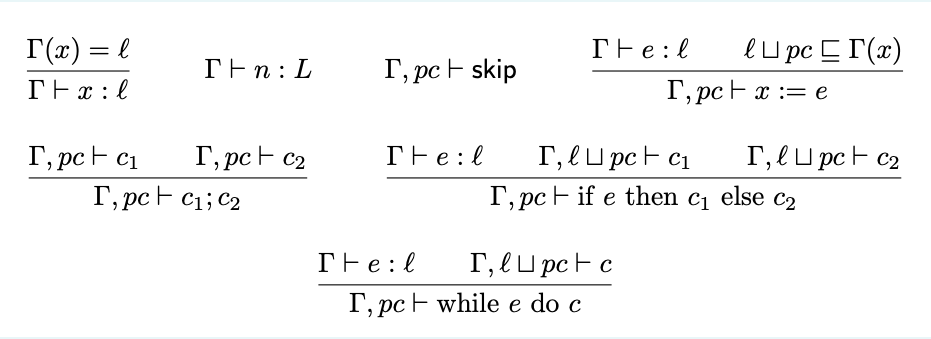
Consider the information flow type system presented during the lecture, shown in the picture below, where we let n range over integers and booleans and e over arithmetic and boolean expressions.
Assume that variables whose name start with the letter h are classified as high (H, secret), while the others are considered as low (L, public). When typing, an expression e cannot be assigned type L if any of its operands has type H.
Which of the following programs would successfully typecheck?
1)
if (l1 < l2) h := true else h := false
2)
h := 5
3)
l := 0; while (h >= l) l := l+1
4)
l := h1 + h2; l := 0
5)
if (h > 0)
if (l1 > l2)
la = l1 - l2
else
la = l2 - l1
else
skip
6)
if (h1 > h2) hmin := h2 else hmin := h1
Note: Solutions can be found at [1]