TU Wien:Software Engineering VU (Christaki)/Exam SE Group A 2025W (2025-12-19)
1.) Formal Modeling (32 Points)[Bearbeiten | Quelltext bearbeiten]
a) Contracts and inheritance (20 Points)
Consider the following interface and its implementations , , and :
trait Display {
method show(port: string, resolution: nat, data: array<char>)
returns (energyUsage: nat)
requires port == “HDMI” || port == “VGA”
requires data.length >= resolution
ensures 20 < energyUsage <= 40
}
// 1
trait Beamer extends Display {
method show(port: string, resolution: nat, data: array<char>)
returns (energyUsage: nat)
requires port == “HDMI”
requires data.length >= 2*resolution
ensures energyUsage == 40
}
// 2
trait Laptop extends Display {
method show(port: string, resolution: nat, data: array<char>)
returns (energyUsage: nat)
requires data.length == resolution
ensures energyUsage == 20
}
// 3
trait TV extends Display {
method show(port: string, resolution: nat, data: array<char>)
returns (energyUsage: nat)
requires port == “HDMI” || port ==
"DisplayPort" || port == “VGA”
requires data.length >= 0
ensures 30 <= energyUsage < 40
}
// 4
trait Crt extends Display {
method show(port: string, resolution: nat, data: array<char>)
returns (energyUsage: nat)
requires port == “VGA”
requires data.length == 8*resolution
ensures energyUsage <= 40
}
1. For each implementation of the method show, mark only the appropriate cells:
Recall that the type nat in Dafny represents the natural numbers (non-negative integers).
| The precondition ... | The postcondition ... | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Implementation | is weakened | is strengthened | is equally strong | is incomparable | is weakened | is strengthened | is equally strong | is incomparable |
| Beamer | ||||||||
| Laptop | ||||||||
| TV | ||||||||
| Crt | ||||||||
2. Which of the implementations of Display are valid?
☐ Beamer ☐ Laptop ☐ TV ☐ Crt
b) Name two differences between functions and methods in Dafny. (4 Points)
c) Consider the following method loop:
method loop()
{
var x, y := 10, 2;
while x+y >= 0
invariant x == 5*y
{ x:=*; y:=*;}
assert (_____);
}
Which of the following assertions are guaranteed to hold after the loop? (8 points)
For those that are not proven, give possible values for x and y after the loop that violate the assertion.
Note: You should consider the assertion one at a time!
| Assertion | Proven | Not Proven + Values | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| assert(x+y >= 0); | ☐ | ☐ | x := ___ | y := ___ |
| assert(x < -y); | ☐ | ☐ | x := ___ | y := ___ |
| assert(x/5 == y); | ☐ | ☐ | x := ___ | y := ___ |
| assert(x >= 0); | ☐ | ☐ | x := ___ | y := ___ |
2.) Multiple Choice (30 Points)[Bearbeiten | Quelltext bearbeiten]
-
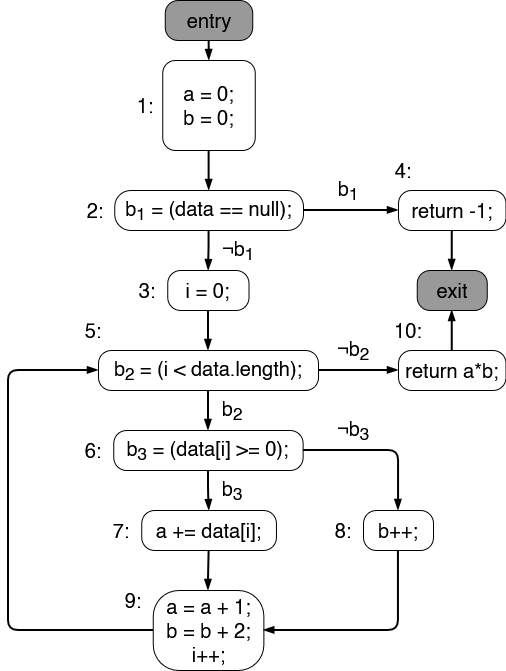
3.) Control-Flow Graph & Control-Flow Coverage (34 Points)[Bearbeiten | Quelltext bearbeiten]
int process(int[] data) {
int a = 0;
int b = 0;
if (data == null) {
return -1;
}
for (int i = 0; i < data.length; i++) {
if (data[i] >= 0) {
a += data[i];
} else {
b++;
}
a = a + 1;
b = b + 2;
}
return a + b;
}
a) Draw the control-flow graph (CFG) for the method . Label all the CFG blocks (excluding and ) from 1 to n, where n is the number of blocks. (16 Points)
b) Answer the following questions about the program and your CFG: (8 Points)
1. How many basic blocks and branches are in your CFG? Do no count the entry and exit blocks.
Basic blocks: ___ Branches: ___
2. How many basic blocks and branches does the input data = {} cover? Compute basic-block coverage and branch coverage (as fractions).
Basic-block coverage: ___ / ___ Branch coverage: ___ / ___
3. Design test cases that achieve 100% branch coverage.
Use as few tests as possible! -1 points per redundant test.
data = ______
data = ______
data = ______
data = ______
data = ______
4. Design test cases that achieve 100% loop coverage.
Use as few tests as possible! -1 points per redundant test.
data = ______
data = ______
data = ______
data = ______
data = ______
c) Prove or refute the following statement: (10 Points)
Given an arbitrary method f, test cases with 100% basic-block coverage always achieve 100% branch coverage.
Either prove the statement by negating it and deriving a contradiction or refute the statement by providing a small counter-example in form of a CFG and inputs.
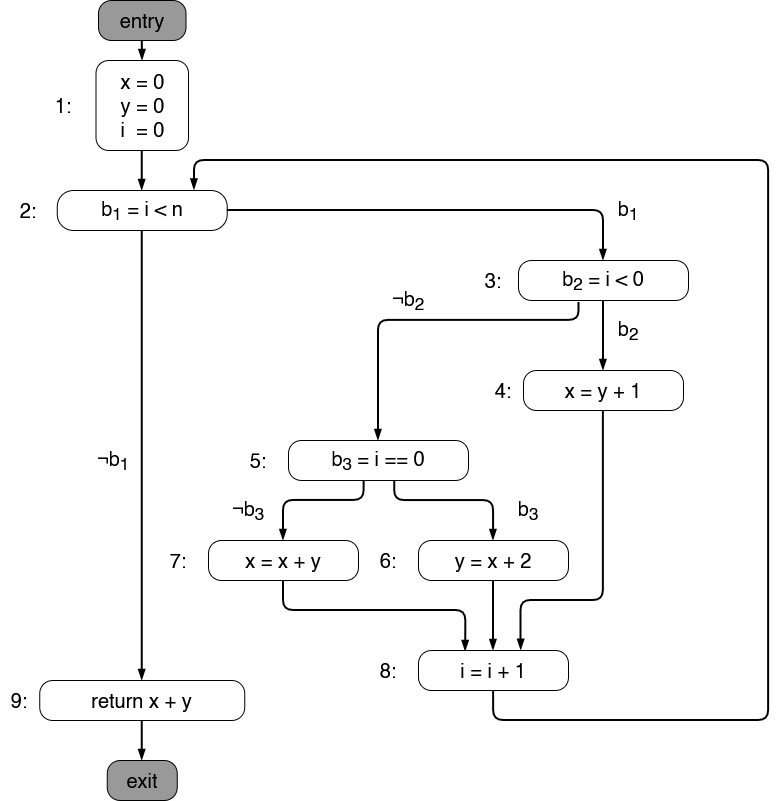
4.) Data-Flow Coverage (34 Points)[Bearbeiten | Quelltext bearbeiten]
int transform(int n) {
int x = 0;
int y = 0;
int i = 0;
while (i < n) {
if (i < 0) {
x = y + 1;
} else if (i == 0) {
y = x + 2;
} else {
x = x + y;
}
i = i + 1;
}
return x + y;
}
a) Apply the algorithm for computing reaching definitions for variables x, y and i, where n is the block number in the control-flow graph. (18 Points)
| n | Reach(n) | ReachOut(n) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | ∅ | |
| 2 | ||
| 3 | ||
| 4 | ||
| 5 | ||
| 6 | ||
| 7 | ||
| 8 | ||
| 9 |
b) List the definitions-use pairs for variables x and y. (10 Points)
Hint: Use as many lines as you need!
| Definition Block | Use Block |
|---|---|
| Definition Block | Use Block |
|---|---|
c) Consider the given test suite below. For each row, compute the Du-Pairs for variable y and write them into the provided column. Finally, compute the DU-Pair coverage (as fraction) for y. (6 Points)
| Test Cases | DU-Pairs for y |
|---|---|
| n = 0 | |
| n = 1 | |
| n = 2 |
DU-pairs coverage for y: ___ / ___ × 100%
5.) Unit Testing (20 Points)[Bearbeiten | Quelltext bearbeiten]
You run an online Christmas-decoration shop that offers standard and express shipping. By default, standard shipping costs 5 euros, while express shipping costs 20 euros. For baskets totals of 100 euros or more, default shipping is free and express shipping costs 10 euros. For totals of 200 euros or more, all shipping is free. You are looking to test the method
int addShippingCost(int basketTotal, boolean isExpress)
throws IllegalArgumentException
It takes as input the basket total (in euros) and returns the total with shipping costs added. The Boolean flag indicates whether the customer selected standard (=) or express shipping (=). If the basket total is negative, an is thrown.
a) List the partitions for each parameter as, respectively, sets of (closed) intervals and values. (12 Points)
Note: You can assume that the basket total does not have a decimal part (no cents).
Note: Use as many lines as you need! Use to denote an interval that is unbounded on one side.
basketTotal: {
[___,___], [___,___], [___,___], [___,___], [___,___],
[___,___], [___,___], [___,___], [___,___], [___,___]
}
express: {____, ____, ____, ____}
b) For which partitions of does the output of not depend on the value of ? (4 points)
c) How many partitions are there total, after combining the partitions of both inputs and merging redundant partitions? (4 points)
Show your calculation!
Solutions:[Bearbeiten | Quelltext bearbeiten]
1.) Formal Modeling[Bearbeiten | Quelltext bearbeiten]
a) 1.
| The precondition ... | The postcondition ... | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Implementation | is weakened | is strengthened | is equally strong | is incomparable | is weakened | is strengthened | is equally strong | is incomparable |
| Beamer | X | X | ||||||
| Laptop | X | X | ||||||
| TV | X | X | ||||||
| Crt | X | X | ||||||
2. ☐ Beamer ☐ Laptop ☑ TV ☐ Crt
b) E.g. functions are deterministic, pure, don't have local variables, a return variable or loops.
c)
| Assertion | Proven | Not Proven + Values | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| assert(x+y >= 0); | ☐ | ☑ | x := -5 | y := -1 |
| assert(x < -y); | ☑ | ☐ | x := ___ | y := ___ |
| assert(x/5 == y); | ☑ | ☐ | x := ___ | y := ___ |
| assert(x >= 0); | ☐ | ☑ | x := -5 | y := -1 |
2.) Multiple Choice[Bearbeiten | Quelltext bearbeiten]
-
3.) Control-Flow Graph & Control-Flow Coverage[Bearbeiten | Quelltext bearbeiten]
a)
b) 1. Basic blocks: 10 Branches: 6
2. Basic-block coverage: 5 / 10 Branch coverage: 2 / 6
3.
data = null
data = {-1, 1}
4. NOTE: This subtask is not fully complete! If you know the correct answer, please consider adding it.
data = {}
data = {1}
c) Not true
E.g.:
Input: n = 1
Here we cover 100% of all basic blocks. However, we do not cover branch .
4.) Data-Flow Coverage[Bearbeiten | Quelltext bearbeiten]
a)
| n | Reach(n) | ReachOut(n) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | ∅ | |
| 2 | ||
| 3 | ||
| 4 | ||
| 5 | ||
| 6 | ||
| 7 | ||
| 8 | ||
| 9 |
b)
| Definition Block | Use Block |
|---|---|
| 1 | 7 |
| 4 | 7 |
| 7 | 7 |
| 1 | 6 |
| 4 | 6 |
| 7 | 6 |
| 1 | 9 |
| 4 | 9 |
| 7 | 9 |
| Definition Block | Use Block |
|---|---|
| 1 | 4 |
| 6 | 4 |
| 1 | 7 |
| 6 | 7 |
| 1 | 9 |
| 6 | 9 |
c)
| Test Cases | DU-Pairs for y |
|---|---|
| n = 0 | (1, 9) |
| n = 1 | (6, 9) |
| n = 2 | (6, 7); (6, 9) |
DU-pairs coverage for y: 3 / 6 × 100%
5.) Unit Testing[Bearbeiten | Quelltext bearbeiten]
a)
basketTotal: {
[-∞, -1], [0, 99], [100, 199], [200, +∞]
}
express: {true, false}
b) [, -1] and [200, ]
c) Initially there are 4 * 2 = 8 partitions. However, since does not affect two of them, we can merge those:
- [, -1] and , [, -1] and => [, -1] and X
- [200, ] and , [200, ] and => [200, ] and X
So, the total after merging is 6.